Table of Contents
Table of Contents
Introduction
Electricity powers our modern world, but not all the energy flowing through our circuits is used in the same way. When you switch on a lamp, the light you see is the result of active energy—the portion of electrical energy that performs useful work. Yet, behind the scenes, another type of energy is constantly circulating: reactive energy. While it doesn’t directly produce light or heat, reactive energy plays a crucial role in maintaining voltage levels and enabling the proper functioning of AC circuits.
This is where the concept of a Reactive Energy Converter comes into play. By understanding reactive energy and how it interacts with active energy, engineers, students, and energy professionals can optimize power systems, reduce losses, and improve efficiency. In this article, we’ll explore what reactive energy is, how it differs from active energy, why it matters in AC circuits, and how a Reactive Energy Converter can help manage it.
What is Reactive Energy in Electricity?
Keyword focus: “what is reactive energy in electricity”
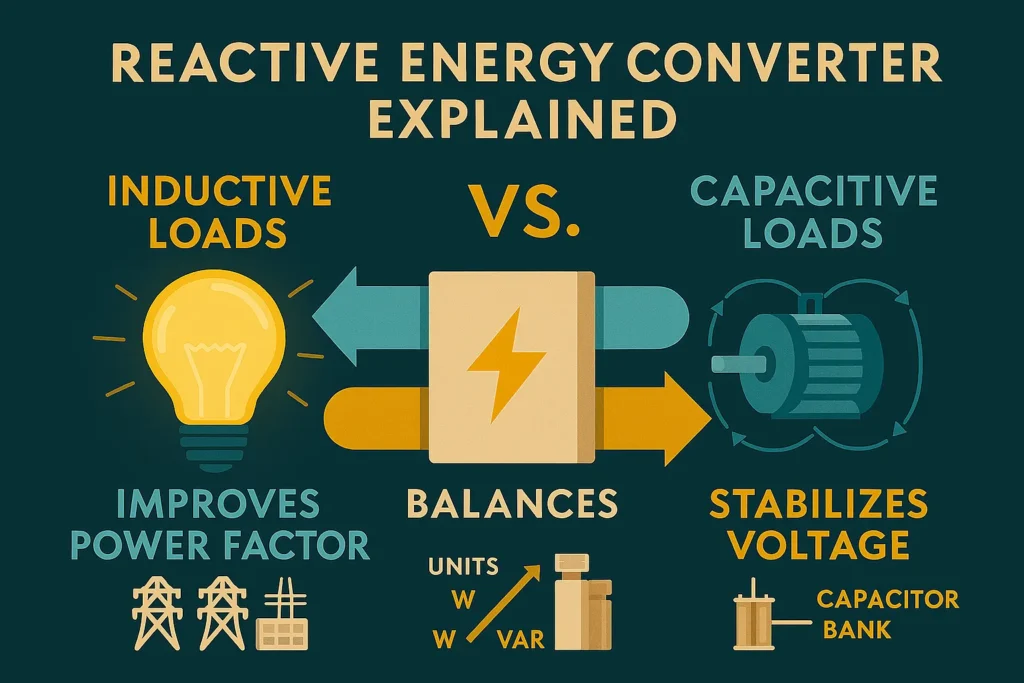
Reactive energy refers to the portion of electrical energy that oscillates back and forth between the source and the load without being consumed. Unlike active energy, which is converted into useful work (like motion, heat, or light), reactive energy is associated with the magnetic and electric fields created by inductive and capacitive components in a circuit.
- Inductive loads (motors, transformers, coils) store energy in magnetic fields.
- Capacitive loads (capacitors, certain electronics) store energy in electric fields.
This stored energy is released back into the system during each cycle, creating a continuous exchange. While reactive energy doesn’t perform useful work, it is essential for maintaining voltage stability and enabling the transfer of active energy.
Example:
Imagine water flowing through a pipe. Active energy is like the water that reaches the destination and is used. Reactive energy is like the water that sloshes back and forth, ensuring pressure is maintained so the flow continues smoothly.
Active Energy vs Reactive Energy
Keyword focus: “active energy vs reactive energy”
To fully grasp the importance of reactive energy, it’s helpful to compare it directly with active energy.
Comparison Table: Active vs Reactive Energy
| Aspect | Active Energy (Real Power) | Reactive Energy (Reactive Power) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Energy that performs useful work | Energy that oscillates between the source and the load |
| Unit | Watt (W) | Volt-Ampere Reactive (VAR) |
| Function | Energy that oscillates between the source and load | Maintains voltage, supports magnetic/electric fields |
| Examples | Light bulbs, heaters, appliances | Motors, transformers, capacitors |
| Impact on System | Directly consumed by devices | Circulates, doesn’t get consumed |
| Importance | Essential for productivity | Essential for system stability |
Why This Matters for SEO
Searchers often type queries like “difference between active and reactive energy”. By presenting a clear table and explanation, your article can rank for comparison-based searches, which Google favors for featured snippets.
Reactive Power in AC Circuits
Keyword focus: “reactive power in AC circuit”
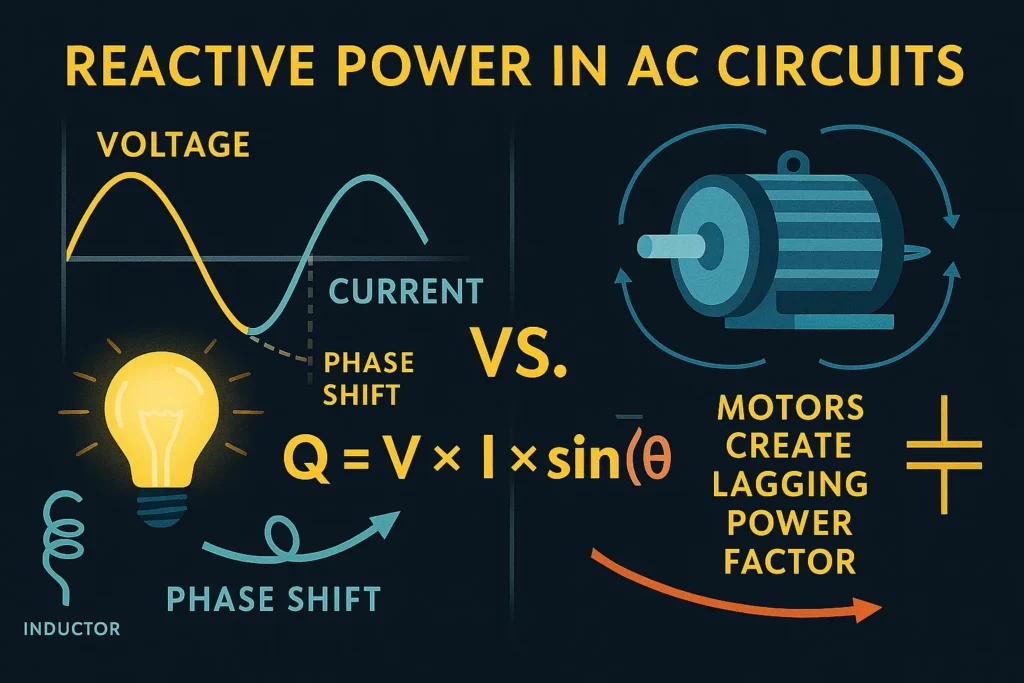
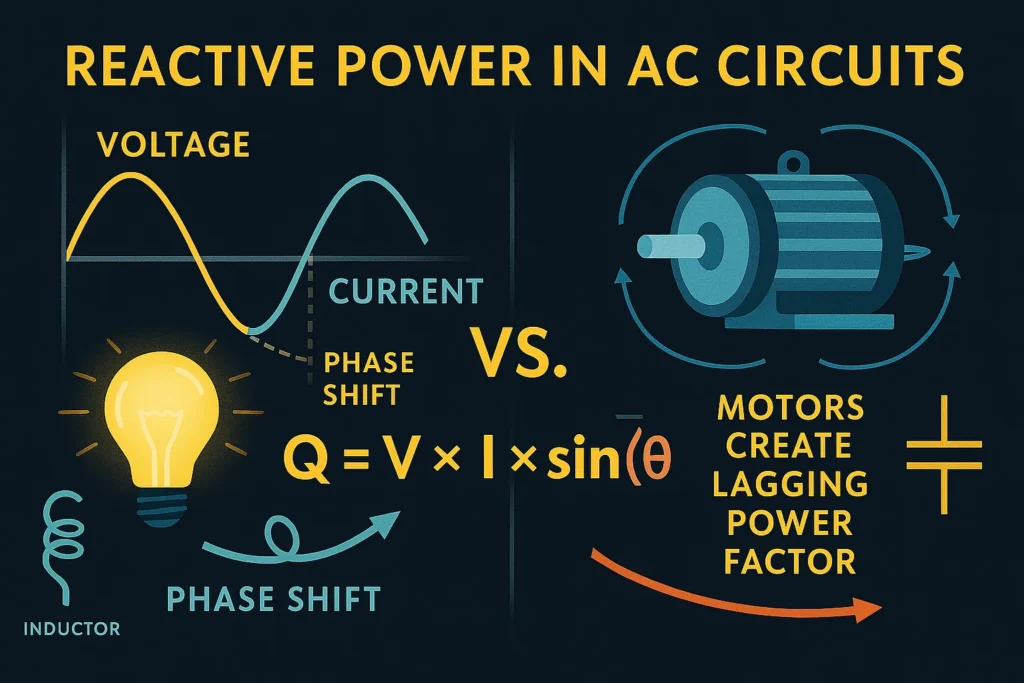
In alternating current (AC) systems, voltage and current are not always perfectly aligned. When they are in phase, all the energy is active. But when there’s a phase difference—caused by inductive or capacitive loads—part of the energy becomes reactive.
Formula:
Q=V×I×sin(ϕ)
Where:
- 𝑄 = Reactive Power (measured in VAR)
- 𝑉 = Voltage
- 𝐼 = Current
- 𝜙 = Phase angle between voltage and current
Practical Example:
- In a motor, the current lags behind the voltage due to inductance.
- This lag creates reactive power, which doesn’t produce mechanical work but is necessary for the motor’s magnetic field.
Without reactive power, AC circuits would collapse because voltage could not be sustained.
Reactive Power Unit (VAR)
Keyword focus: “reactive power unit”
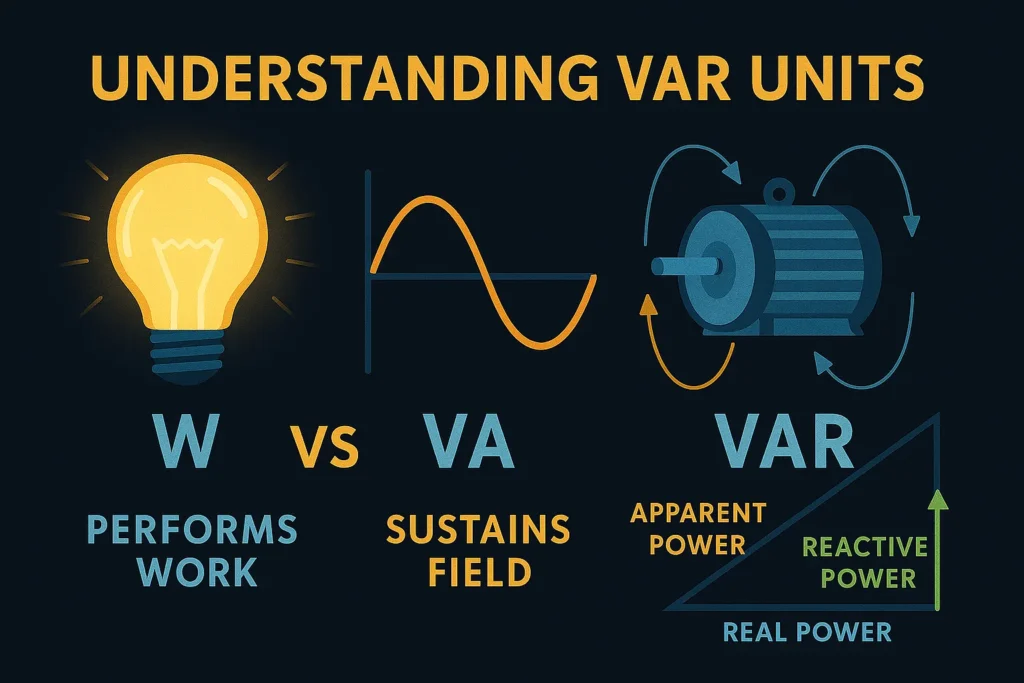
Reactive power is measured in Volt-Ampere Reactive (VAR). This unit distinguishes reactive energy from active energy, which is measured in watts.
- 1 VAR represents one volt-ampere of reactive power.
- Large industrial systems often deal with kVAR (kilovolt-ampere reactive) or MVAR (megavolt-ampere reactive).
Reactive power is measured in Volt-Ampere Reactive (VAR), which distinguishes it from active energy measured in watts. Utilities monitor reactive power because excessive reactive energy reduces system efficiency, and engineers often use capacitor banks to balance reactive loads.
For a deeper dive into practical applications, check out our detailed guide: Reactive Power Converter – Free Online Tool.
Why VAR Matters
- Utilities monitor reactive power because excessive reactive energy reduces system efficiency.
- Engineers use VAR calculations to design compensation systems, such as capacitor banks, to balance reactive loads.
By including this keyword-rich section, your article can rank for technical queries like “reactive power unit explained”.
What is a Reactive Energy Converter?
Keyword focus: “Reactive Energy Converter”
A Reactive Energy Converter is a conceptual or practical tool designed to manage reactive energy in electrical systems. While reactive energy itself cannot be directly consumed, converters and compensators can transform its impact on the system by:
- Balancing loads: Ensuring inductive and capacitive effects cancel each other.
- Improving efficiency: Reducing unnecessary circulation of reactive energy.
- Voltage stabilization: Helping maintain consistent voltage levels in AC networks.
- Power factor correction: Converting reactive energy effects into a more favorable balance between active and reactive power.
A Reactive Energy Converter is a conceptual or practical tool designed to manage reactive energy in electrical systems. While reactive energy itself cannot be directly consumed, converters and compensators can transform its impact on the system by balancing loads, improving efficiency, stabilizing voltage, and correcting power factor.
👉 You can try this concept in practice using our free online tool: Reactive Energy Converter Tool, available in the tools section of our website.
Applications of Reactive Energy Converters
- Industrial plants: Managing large motors and transformers.
- Power grids: Stabilizing voltage across transmission lines.
- Renewable energy systems: Ensuring solar and wind installations maintain grid compatibility.
By focusing on this keyword, your article establishes authority around your tool and brand, making it easier to rank for niche searches.
Why Reactive Energy Matters for Efficiency
Reactive energy may seem like wasted energy, but it’s vital for the health of electrical systems. However, too much reactive energy can cause inefficiencies.
- High reactive power → low power factor → wasted capacity.
- Balanced reactive power → stable voltage → efficient system.
Example Table: Impact of Reactive Energy on Power Factor
| Power Factor | Reactive Energy Level | System Impact |
|---|---|---|
| 1.0 (Ideal) | Zero reactive energy | Maximum efficiency |
| 0.8 | Moderate reactive energy | Increased losses, reduced capacity |
| 0.6 | High reactive energy | Poor efficiency, unstable voltage |
This section helps target queries like “why is reactive energy important” and “reactive power efficiency”.
How a Reactive Energy Converter Helps
The Reactive Energy Converter acts as a bridge between theory and practice. By managing reactive energy, it enables:
- Power factor correction → Lower electricity bills for industries.
- Voltage regulation → Stable supply for sensitive equipment.
- Reduced transmission losses → More efficient grid operation.
- Improved reliability → Less strain on generators and transformers.
This positions your tool not just as a calculator but as a solution-oriented utility.
Conclusion
Reactive energy may not light a bulb or spin a fan, but it is the invisible backbone of AC power systems. Without it, voltage stability would collapse, and active energy could not flow effectively. By understanding the difference between active and reactive energy, recognizing the role of VAR units, and applying concepts like the Reactive Energy Converter, engineers and students can unlock new levels of efficiency and reliability in electrical systems.
For your site, this article does more than explain—it builds authority. With “Reactive Energy Converter” as the focus keyword and supporting terms like “reactive power in AC circuit” and “active vs reactive energy”, you’ll attract both niche technical readers and broader educational audiences.
In short, the Reactive Energy Converter isn’t just a tool—it’s a gateway to understanding how electricity truly works.
❓ Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is a Reactive Energy Converter?
A Reactive Energy Converter is a tool or system designed to manage reactive energy in electrical circuits. It helps balance inductive and capacitive loads, improves voltage stability, and supports power factor correction. By using a converter, engineers can reduce transmission losses and optimize efficiency in AC networks.
2. What is reactive energy in electricity?
Reactive energy in electricity is the portion of energy that oscillates between the source and the load without being consumed. It is linked to the magnetic fields of inductors and the electric fields of capacitors. While it doesn’t perform useful work like active energy, it is essential for maintaining voltage levels in AC circuits.
3. What is the difference between active energy and reactive energy?
– Active energy (measured in watts) performs useful work such as lighting, heating, or motion.
– Reactive energy (measured in VAR) circulates between the source and load, supporting voltage and magnetic/electric fields. Both are necessary: active energy powers devices, while reactive energy ensures the system operates reliably.
4. What is reactive power in an AC circuit?
Reactive power in an AC circuit is the energy associated with the phase difference between voltage and current. It is measured in Volt-Ampere Reactive (VAR) and is crucial for sustaining the magnetic and electric fields in motors, transformers, and capacitors. Without reactive power, AC circuits would lose voltage stability.
5. What is the unit of reactive power?
The unit of reactive power is the Volt-Ampere Reactive (VAR). Larger systems often use kVAR (kilovolt-ampere reactive) or MVAR (megavolt-ampere reactive). This unit distinguishes reactive energy from active energy, which is measured in watts.
6. Why is reactive energy important in electricity?
Reactive energy is important because it maintains voltage stability and allows active energy to flow effectively. Without reactive energy, motors, transformers, and other inductive loads could not function properly. However, excessive reactive energy reduces efficiency, which is why converters and compensation systems are used.
7. How does a Reactive Energy Converter improve efficiency?
A Reactive Energy Converter improves efficiency by:
– Correcting power factor
– Reducing transmission losses
– Stabilizing voltage levels
– Balancing inductive and capacitive loads This ensures that more of the supplied energy is used as active energy, lowering costs and improving reliability.
8. What is the relationship between reactive power and power factor?
Power factor is the ratio of active power to apparent power. High reactive power lowers the power factor, meaning more energy circulates without doing useful work. By managing reactive power with converters or capacitor banks, the power factor can be improved, leading to better efficiency.
9. Can reactive energy be converted into active energy?
Reactive energy itself cannot be directly converted into active energy because it doesn’t perform useful work. However, a Reactive Energy Converter or compensation system can minimize its negative effects, balance loads, and improve the overall efficiency of active energy usage.
10. Where can I use a Reactive Energy Converter online?
You can use our free tool here: Reactive Energy Converter Tool. It allows you to calculate and understand reactive energy in practical scenarios. For related calculations, explore our Reactive Power Converter Tool.